Adversity in childhood is linked to increased risk of heart and blood vessel diseases in early adulthood

[ad_1]
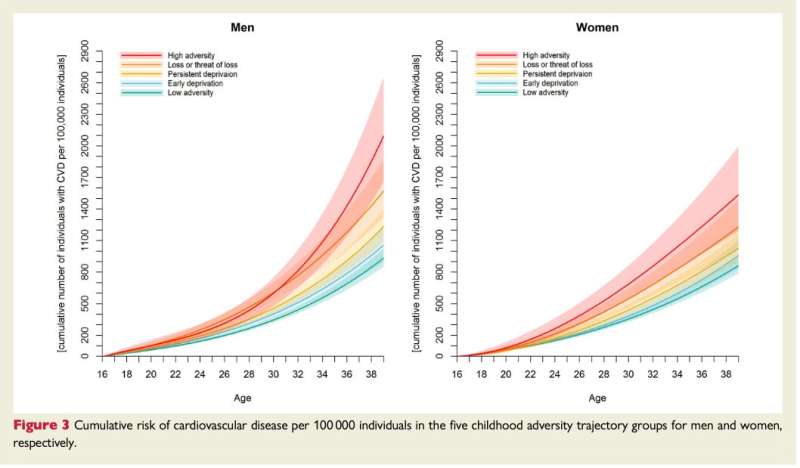
Youngsters who expertise adversity, together with severe household sickness or loss of life, poverty, neglect, or dysfunctional and nerve-racking household relationships, are at elevated threat of creating illnesses of the center or blood vessels in early maturity.
The brand new analysis, which is printed within the European Coronary heart Journal at present, is the most important examine thus far to take a look at the hyperlinks between childhood adversity and heart problems (CVD). It adopted almost 1.3 million kids, born between January 1980 and December 2001, up till 31 December 2018. Throughout this time 4,118 developed CVD between their sixteenth birthdays and the tip of 2018, by which era the oldest had been 38 years previous.
Senior writer of the examine, Professor Naja Hulvej Rod, head of epidemiology on the Division of Public Well being on the College of Copenhagen, mentioned, “In comparison with younger adults who skilled little adversity in childhood, we discovered an roughly 60% larger threat of creating heart problems amongst younger adults who had skilled adversity.
“This was very true for individuals who had skilled severe diseases, akin to most cancers, coronary heart or lung illnesses, or loss of life within the household, and people who had skilled excessive and accelerating ranges of adversity in childhood. In absolute numbers, this corresponds to 10–18 further circumstances of CVD per 100,000 person-years. For comparability, the typical incidence fee of CVD amongst a 30-year-old individual is roughly 50 circumstances of CVD per 100,000 person-years.”
The researchers used knowledge from the DANish LIFE course (DANLIFE) cohort, which incorporates repeatedly recorded data from quite a few nationwide registers. They recognized 1,263,013 kids who had been alive and residing in Denmark till their sixteenth birthdays and who weren’t recognized with CVD or congenital coronary heart illness throughout this time.
They divided them into 5 teams based mostly on adversity skilled between the ages of 0 and 15:
- People who skilled low adversity throughout childhood,
- Adolescence materials deprivation (as an illustration, poverty and long-term unemployment within the household throughout youth),
- Persistent deprivation (materials deprivation skilled via into adolescence),
- Loss or menace of loss (excessive charges of significant sickness or loss of life amongst dad and mom or siblings)
- Excessive adversity (protecting publicity to any or the entire earlier varieties of adversity, notably dysfunctional and nerve-racking household relationships, skilled on common yearly throughout adolescence)
The researchers adjusted their analyses to take account of things that might additionally improve the danger of CVD, akin to age, maternal age at beginning, parental origin, and any parental illnesses of the center, blood vessels or metabolism. In supplementary analyses, additionally they adjusted for gestational age and parental schooling. They excluded folks whose dad and mom had an sickness associated to the center or metabolism, akin to diabetes or coronary heart illness, which could predispose their kids to creating these circumstances.
The researchers discovered there was little distinction within the threat of creating CVD between the two,195 males and 1,923 ladies within the examine. The chance was highest amongst individuals who skilled extreme sickness or loss of life within the household and amongst those that skilled excessive and rising charges of adversity all through childhood and adolescence.
Prof. Rod mentioned, “The affiliation we noticed between childhood adversity and CVD in early maturity could also be defined partly by behaviors that may have an effect on well being, akin to consuming alcohol, smoking and bodily inactivity. Childhood is a delicate interval characterised by fast cognitive and bodily developments; the frequent and continual publicity to adversity in childhood might affect the event of the physiological stress response, and this will likely present an vital clarification for the mechanisms underlying these findings.”
The researchers plan to research the potential underlying mechanisms for his or her findings in order to know the affect of childhood adversity on CVD prognosis and survival. This can embrace entry to well being care, potential non-compliance with remedies, and different well being issues amongst kids from socially troublesome backgrounds. The present examine has constructed on earlier work the researchers carried out that confirmed a considerably larger threat of untimely mortality, together with deaths as a result of CVD, and hospitalizations due CVD amongst younger adults, who had skilled adversity in childhood and adolescence.
Prof. Rod mentioned, “The incidence of CVD is low in early grownup life, however will increase considerably throughout this era. This highlights the significance of analysis into non-genetic youth threat components, which can be focused for early prevention. The expertise of adversity is widespread amongst kids, and on this examine we present that kids who expertise long-term and extreme stress from severe diseases and loss of life within the household, and youngsters who’re uncovered to excessive charges of adversity, together with deprivation, household loss, and dysfunctional and nerve-racking household relationships, have a better threat of creating CVD in early maturity. Concentrating on the social origins of such adversity and making certain supportive buildings for households who’re—for instance—combating illness within the household, might probably carry long-term protecting results.”
Professor Gunnar Gislason, head of analysis on the Danish Coronary heart Affiliation, commented, “We all know far too little in regards to the connection between early trauma and stress in childhood and the danger of heart problems later in life. That’s the reason this venture is so vital, as it could probably reveal one of many explanations for the social inequality in heart problems.”
Jessica Bengtsson et al, Childhood adversity and heart problems in early maturity: a Danish cohort examine, European Coronary heart Journal. DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac607
European Society of Cardiology
Quotation:
Adversity in childhood is linked to elevated threat of coronary heart and blood vessel illnesses in early maturity (2022, November 14)
retrieved 14 November 2022
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2022-11-adversity-childhood-linked-heart-blood.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.
[ad_2]




